Diffuse hair loss: How it occurs and what measures help
What is diffuse hair loss?
Diffuse hair loss is when the hair on the head thins out overall and the scalp shines through more than usual. Signs of this are that more than 100 hairs are shed every day.
Sometimes the hair loss is more noticeable on the temples, on the front of the head and in the crown area.
Unlike hereditary or circular hair loss, diffuse hair loss usually does not cause bald patches to form. It also doesn't happen that the hair falls out completely.
Usually there is a triggering event
The causes of hair loss are very different. For example, hormonal changes, certain diseases, nutrient deficiencies or the use of some medications can trigger diffuse hair loss. Sometimes no trigger can be found.
Hair can grow back
Usually, hair loss begins two to three months after the triggering event. It takes between six to twelve months for the hair to grow back visibly.
Sometimes it can happen that the hair loss lasts four to six months or longer.
Hair increasingly goes into a resting state
Hair goes through a life cycle. First they grow, then they rest and finally they fall out. The hair goes through these phases at different times. Normally, about 10 percent of all scalp hair is in the resting phase. In the case of diffuse hair loss, this affects up to 35 percent. This means that the hair goes into the resting phase prematurely.
Diffuse hair loss in cancer and poisoning
Hair loss also occurs as a side effect of chemotherapy or radiation. Such treatments damage healthy tissue that grows quickly and can renew itself – like hair.
As a result of the therapy, the growing hairs atrophy and fall out one to four weeks later. This usually happens very quickly and over a large area. As a rule, in addition to the hair on the head, it also affects eyebrows, eyelashes and pubic hair.
In some cases, the hair breaks off a few millimeters above the scalp. They are therefore colloquially called "exclamation mark hair".
Poisoning, for example with heavy metals such as thallium or cadmium, can also lead to rapid hair loss. In most cases, other symptoms of poisoning occur, such as nausea and vomiting, cramps or paralysis.
As soon as the therapy is finished or the poisoning is treated, the hair begins to grow again.

Cancer therapy: When does hair fall out, what can I do?
Cancer treatments are often accompanied by hair loss: when it can happen, what the causes are.Details
What are the causes of diffuse hair loss?
There are various factors, influences and diseases that can trigger diffuse hair loss. In some of the affected people, the cause is unclear.
- Acute stress situations. These include serious operations, injuries or psychological stress.
- Birth. While many pregnant women's hair grows more and becomes thicker, the opposite happens after childbirth: the hair falls out more than usual.
- Menopause. During menopause, the amount of the female sex hormone estrogen decreases. This can be noticeable in the form of hair loss.
- Contraception with hormones. Women who use the contraceptive pill and stop taking it sometimes observe increased hair loss.
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the scalp. They can be the cause of diffuse hair loss. These include, for example, head fungus (tinea capitis), bacterial infections of the scalp such as hair folliculitis, seborrheic eczema or psoriasis.
- Diseases of the endocrine system. These include, for example, the underactive or overactive thyroid gland. With an underactive thyroid, dull, brittle hair or hair loss can occur, in addition to many other symptoms such as dry skin. An overactive thyroid can show up in addition to symptoms such as warm, moist skin with soft, thin hair and diffuse hair loss.
- febrile infectious diseases. Diseases caused by viruses such as flu or Covid-19 can be associated with hair loss.
- chronic diseases. for example, the liver or the hematopoietic system.
- Taking medication. Hair loss can occur as a side effect of medication. These include, for example, blood thinners, cholesterol-lowering drugs or certain drugs for high blood pressure. If there is a suspicion, you should never stop taking the medication on your own, but always discuss with your doctor whether there is an alternative.
- Nutrient deficiency. A lack of nutrients can trigger hair loss. Possible reasons are, for example, rapid weight loss, an unbalanced diet, diet, eating disorder, iron or zinc deficiency.
Course of diffuse hair loss
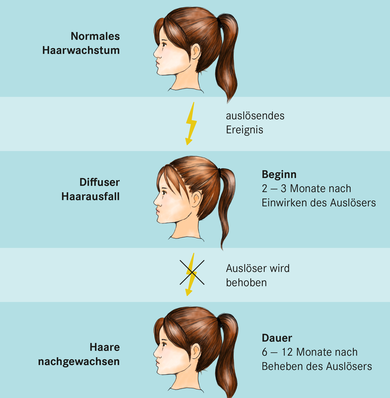
If you find the trigger for diffuse hair loss and can remedy it, the hair will grow back within half a year to a whole year.
© W&B/Astrid Zacharias
How is diffuse hair loss diagnosed?
In order to determine diffuse hair loss, a detailed discussion and a physical examination are important.
In people who have naturally full hair, diffuse hair loss is often not recognizable. It can therefore be helpful to take before-and-after photos with you when you visit your doctor.
Medical consultation
In the conversation, the doctor will ask various questions about the life situation, eating habits and medical history. For example, the aim is to find out whether you:
- was last acutely ill and had a fever
- has a chronic disease, such as skin or liver
- takes medication regularly
- has changed their diet or is on a diet
- is or has been exposed to emotional stress
- with hormonal preparations such as the contraceptive pill and has discontinued them
- gave birth to a child a few weeks ago
Physical examination and blood tests
The doctor examines the hair, scalp and nails. In addition, he or she may use a plucking test to check whether it is active hair loss. In addition, a trichogram can be used to determine how many hairs are in the loss stage.
If there is a suspicion that a lack of minerals such as iron or a thyroid disease has triggered the hair loss, blood tests can help.
If the doctor wants to distinguish hair loss from other forms, an examination with a reflected light microscope (dermatoscope) may be useful.
If the diagnosis is unclear despite a detailed discussion and a detailed examination of the scalp, the removal of tissue (biopsy) can sometimes help.
How can diffuse hair loss be treated?
In order to be able to treat diffuse hair loss, it is important to find and eliminate the trigger.
Which therapy is used always depends on the respective cause:
- If an illness is present, it must be treated accordingly.
- If the intake of medication is the trigger, the attending physician may be able to prescribe another preparation. It is important not to stop taking the medication on your own.
- If the hair loss is caused by a diet, it makes sense to end the diet and switch to a balanced diet.
- If there is a persistent deficiency of nutrients or minerals, the doctor can determine this and, if necessary, prescribe a suitable preparation.
Can remedies for hair loss or a hair transplant help?
Some doctors prescribe minoxidil preparations for application to the skin or to be taken orally. This active ingredient is primarily used for hereditary hair loss. Whether it also helps with diffuse hair loss has not been sufficiently scientifically proven.
Transplanting your own hair is not a suitable measure for people with diffuse hair loss.

Sometimes diffuse hair loss can be concealed by hairstyling.
© Vera Lair / Stocksy United
What can I do if hair loss is bothering me?
If you feel uncomfortable with hair loss, you can hide (conceal) it in various ways.
If the hair loss is very stressful, it makes sense to also contact a psychotherapist.
Headgear, hairpiece or wig
Some people with hair loss choose to wear a headscarf, cap, or hat. Others feel more comfortable concealing hair loss with a hairpiece or wig.
In some cases – such as hair loss due to chemotherapy – the health insurance company covers the costs of hair replacement. It is best to ask in advance.

After cancer therapy: How do I get a wig?
If women need hair replacement because of chemotherapy or radiation therapy, there are a few things to consider.Details
Other cosmetic measures
Sometimes a different hairstyle or special hairstyling ensures that hair loss is less noticeable.
It is also possible to dye the hair with shades that make the thinned hair appear less thin.
There are also various ways to treat the scalp and cover thinning areas.
In order to find a suitable solution for yourself, professional advice is the best first step.
Important note
This article contains only general information and must not be used for self-diagnosis or treatment. It cannot replace a medical consultation. Please understand that we do not answer individual questions.
